Pinworms, those tiny intestinal parasites notorious for afflicting humans, have a broader reach in the animal kingdom than one might think. While often discussed concerning human health, pinworms are not exclusive to our species. Many animals, both domestic and wild, can harbor these parasitic invaders. This article aims to shed light on the often-overlooked aspect of animals That Can Get Pinworms.
From household pets to wildlife, we’ll delve into the curious world of which animals can become hosts to pinworms, exploring their lifecycle, potential health impacts, and the importance of understanding and managing these delicate intruders to ensure the well-being of both animals and humans. Join us on this informative journey through the lesser-known domain of pinworm infestations in diverse animal species.
Table of Contents
Explanation of Pinworms and Their Significance in Animal Health:
Pinworms, or Enterobius vermicularis, are small, thread-like parasitic worms that infest the gastrointestinal tract of various animals, including humans. While they predominantly affect humans, pinworms are also significant in animal health. These parasites can cause gastrointestinal discomfort, irritation, and potentially more severe health issues, impacting an animal’s overall well-being.
The importance of understanding pinworms lies in effective prevention, management, and treatment to ensure the health and vitality of both domestic and wild animals. Proper awareness and measures to control and mitigate pinworm infestations are essential for maintaining optimal animal health.
What Are Pinworms?
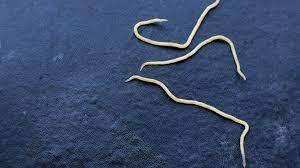
Pinworms, scientifically known as Enterobius vermicularis, are small, thread-like parasitic worms that commonly infest the intestines of various animals, including humans. They belong to the group of parasites called helminths and are typically white, thread-like worms. These parasites are significant in animal health as they can lead to gastrointestinal issues, nutritional deficiencies, discomfort, and, in severe cases, can affect an animal’s overall well-being. Understanding pinworms and their impact on animals is crucial for effective prevention, management, and maintaining the health of both domestic and wild creatures.
Common Animals Hosting Pinworms:
Horses: Equine species, especially horses, are commonly affected by pinworms. The infestation can cause irritation and discomfort in the horse’s rectum and colon, affecting their overall health and performance.
Dogs: Canine companions can also harbor pinworms, which can lead to digestive problems, including diarrhea and vomiting.
Cats: Feline friends can experience pinworm infestations, affecting their gastrointestinal tract and potentially causing health issues.
Rabbits: Pinworms are prevalent in rabbits, particularly in young individuals. Infestations can hinder growth and lead to digestive disturbances.
Guinea Pigs: These small pets can host pinworms, impacting their digestive health and general well-being.
Transmission and Spread of Pinworms:
Pinworms typically spread through ingestion or inhalation of pinworm eggs. Contaminated food, water, feces, and contaminated surfaces can act as sources of infection. Animals can contract pinworms from infected feces, contaminated bedding, or through grooming and direct contact with infected individuals. Maintaining proper hygiene and sanitation practices is vital to reduce the spread of pinworms.

Health Implications of Pinworm Infestations:
Pinworm infestations can have various health implications for animals. These include irritation and inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to discomfort, colic, diarrhea, weight loss, and a decrease in overall health and performance. In severe cases or when left untreated, pinworms can cause malnutrition, intestinal blockages, and compromise the immune system. Understanding the potential health impacts of pinworm infestations is crucial for early detection, appropriate treatment, and overall animal well-being.
Prevention and Control Measures:
Preventing and controlling pinworm infestations involves a multifaceted approach. This includes maintaining good hygiene practices, proper sanitation, routine deworming, regular veterinary check-ups, and implementing effective biosecurity measures.
Strategies such as proper waste disposal, cleaning and disinfection of living spaces, and minimizing animal exposure to contaminated environments are essential in preventing pinworm infections. Education and awareness regarding the importance of these measures are vital for both animal caretakers and the community to ensure a healthy living environment for animals.

Treatment and Management of Pinworm Infestations:
Treating and managing pinworm infestations in animals involves using appropriate anthelmintic medications. These medications are specifically designed to target and eliminate pinworms from the gastrointestinal tract. The treatment regimen, dosage, and administration guidelines vary based on the animal species, the severity of the infestation, and the specific anthelmintic used. Monitoring and follow-up after treatment are essential to assess treatment effectiveness and ensure complete eradication of the parasites.
Zoonotic Potential: Can Humans Get Pinworms from Animals?
While pinworms are primarily considered human parasites, there is a limited zoonotic potential, meaning that some pinworm species can potentially infect both humans and animals. However, the risk of zoonotic transmission is relatively low compared to the risk of human-to-human transmission.
Nevertheless, individuals in close contact with infected animals should observe proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing, to minimize the risk of potential zoonotic transmission. Understanding the zoonotic potential of pinworms is crucial for promoting safe practices and minimizing health risks associated with animal-human interactions.

Final Words
In conclusion, understanding pinworms and their significance in both animal and human health is vital for promoting overall well-being. Pinworm infestations can affect a range of animals, from horses and dogs to cats, rabbits, and guinea pigs, causing gastrointestinal discomfort and potentially leading to more severe health issues. To mitigate these concerns, preventive measures such as proper hygiene, routine veterinary care, and deworming protocols are crucial.
Effective treatment and management strategies play a pivotal role in eradicating pinworm infestations and ensuring the health and vitality of animals. While there is a limited zoonotic potential for pinworm transmission between animals and humans, maintaining good hygiene practices is essential for minimizing any associated risks. By raising awareness about pinworms and implementing preventive and control measures, we can create a safer environment for both animals and humans, promoting a harmonious coexistence with these delicate intestinal intruders.
Reference:
- https://wsava.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Clinician-s-Brief-February-2018-TP-Pinworm.pdf
- https://www.wormsandgermsblog.com/2010/01/articles/animals/dogs/pinworms-and-pets/

Jeevan Kodiyan
An animal enthusiast with an interest in zoology, studying the behavior and activities of animals in the wild habitat. I work on research projects related to species conservation and endangered species protection. I also leverage zoology to become an educator, educating others about the importance of protecting our natural environment and the beauty of animals in their natural habitats.









