The Earth’s continental shelves, submerged extensions of the continents into the vast oceans, are treasure troves of marine biodiversity. Home to a stunning array of creatures, these shelves encompass shallow seas and host ecosystems vital to our planet’s health. From mysterious deep-sea creatures to charismatic megafauna, the continental shelf showcases an incredible diversity of life.
In this exploration, we will delve into the depths to unveil the fascinating world of Animals of the Continental Shelf that inhabit these critical marine habitats. From the kaleidoscopic coral reefs to the abyssal plains, each niche holds unique life forms, each contributing to the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
Table of Contents
Through this journey, we aim to shed light on the importance of preserving and understanding the animals that call the continental shelf their home, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect these extraordinary environments and their inhabitants.
Brief Overview of the Continental Shelf:

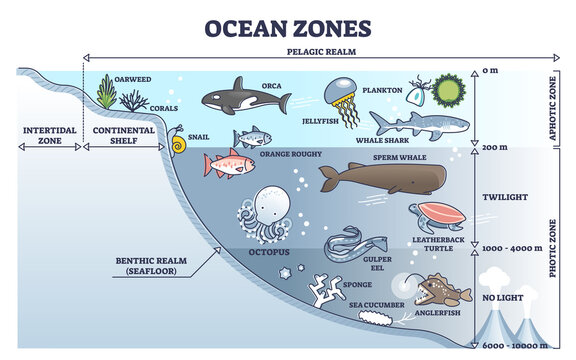
The continental shelf is a pivotal component of the Earth’s oceanic geography, representing the submerged border of each continent extending into the surrounding oceans. It is characterized by shallow waters, extending from the shoreline to the continental slope.
This region hosts an abundance of marine life due to its accessibility to sunlight and proximity to nutrient-rich coastal waters. The breadth of the continental shelf varies across the globe, impacting the diversity of life it supports and its role in the broader marine ecosystem.
The Continental Shelf: A Habitat for Diverse Marine Life:
The continental shelf is a vibrant and vital habitat for a myriad of marine organisms. Its relatively shallow depths, abundant sunlight, and nutrient-rich waters provide an ideal environment for a diverse range of flora and fauna. From colorful coral reefs to vast kelp forests, and from microscopic plankton to magnificent marine mammals, the continental shelf sustains an intricate web of life.
This dynamic ecosystem plays a critical role in marine food chains, supporting populations of fish, crustaceans, and other marine species. Understanding and preserving the biodiversity within the continental shelf is essential for maintaining the health and balance of our oceans.
List Of Animals of the Continental Shelf :
The animal diversity found within the continental shelf is awe-inspiring. It encompasses an extensive array of species, each adapted to its specific niche within this dynamic marine habitat. From bottom-dwelling invertebrates like crabs and sea stars to pelagic species like tuna and dolphins, the continental shelf hosts an astonishing variety of life.
The diversity ranges from sessile organisms like corals and sponges to highly mobile predators like sharks and whales. This rich tapestry of marine life forms the foundation of a complex ecosystem, with each species playing a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of the continental shelf.
Cod:
Cod are iconic fish known for their white, flaky flesh and mild flavor. They inhabit the cold waters of the North Atlantic and are a staple in many cuisines, often used in dishes like fish and chips.
Haddock:
Haddock, another popular North Atlantic fish, resembles cod but has a slightly sweet taste. Its white flesh is tender and used in various dishes, including smoked haddock and fish chowders.
Salmon:
Salmon are prized for their flavorful, pink-orange flesh. They’re known for their incredible journeys, migrating from freshwater to the ocean and back to spawn, an essential process for their life cycle.
Tuna:
Tuna are large, fast-swimming fish highly valued for their meat, often used in sushi and sashimi. They are a key species in the world’s fisheries.
Halibut:
Halibut is a flatfish known for its delicate taste and dense, flaky white flesh. It’s popular in various culinary preparations, from grilling to baking.
Mackerel:
Mackerel are oily fish, known for their distinct flavor. They’re abundant in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans and are often smoked, grilled, or pickled.
Sardines:
Sardines are small, oily fish packed with nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids. They are often canned and enjoyed for their unique taste and health benefits.
Anchovies:
Anchovies are small, oily fish used in many Mediterranean dishes, adding a salty and savory flavor to sauces, salads, and pizzas.
Snapper:
Snapper is a flavorful fish, popular in various cuisines. Its firm, white flesh makes it versatile for grilling, baking, or frying.
Grouper:
Grouper is a sought-after fish, prized for its mild taste and thick, white flesh. It’s a staple in seafood dishes, often grilled or fried.
Whales (e.g., humpback whales, blue whales):
Whales, such as humpback and blue whales, are awe-inspiring marine mammals. Humpback whales are known for their acrobatic displays and haunting songs, while blue whales hold the title of the largest animals on Earth. These gentle giants play a crucial role in marine ecosystems.
Dolphins:
Dolphins are intelligent and social marine mammals, known for their playful behavior and remarkable communication skills. They are often seen leaping and riding the waves alongside boats.
Porpoises:
Porpoises are small, toothed whales closely related to dolphins. They are shy and tend to avoid boats, making them less commonly seen than their dolphin cousins.
Seals:
Seals are semi-aquatic mammals, recognizable by their sleek bodies and playful antics in the water. They are skilled hunters and spend a significant part of their lives at sea.
Sea lions:
Sea lions are pinnipeds known for their barking calls and social behavior. They are excellent swimmers and often seen basking on rocks or beaches.
Crabs:
Crabs are crustaceans with a hard exoskeleton and a sideways gait. They are highly diverse, occupying various habitats and playing crucial roles in marine ecosystems.
Lobsters:
Lobsters are large, marine crustaceans prized for their succulent meat. They are a culinary delicacy, often prepared by boiling or grilling.
Shrimp:
Shrimp are small crustaceans with a sweet and delicate taste. They are a versatile ingredient used in a wide array of dishes globally.
Crawfish:
Crawfish, also known as crayfish or freshwater lobsters, resemble small lobsters and are often enjoyed in Southern cuisine, especially in dishes like crawfish boils.
Clams:
Clams are bivalve mollusks, known for their tender and flavorful meat. They come in various species and are used in a variety of dishes.
Oysters:
Oysters are bivalve mollusks prized for their unique taste and texture. They are often served raw on the half shell, cooked, or used in seafood stews and chowders.
Mussels:
Mussels are bivalve mollusks commonly found in coastal waters. They have a slightly sweet and briny flavor and are used in various dishes, from pasta to soups.
Squid:
Squid, also known as calamari, are cephalopods with a mild, slightly sweet flavor. They are often used in appetizers, stir-fries, and salads.
Octopuses:
Octopuses are highly intelligent and elusive cephalopods known for their problem-solving abilities and unique appearance. They are a delicacy in many cuisines.
Sea stars (starfish):
Sea stars, or starfish, are intriguing marine creatures with their radial symmetry and tube feet. They play a vital role in maintaining balance in marine ecosystems.
Sea urchins:
Sea urchins are spiny, round creatures related to sea stars and sand dollars. They are sought after for their roe, known as uni, a delicacy in sushi.
Sea cucumbers:
Sea cucumbers are echinoderms known for their elongated, cucumber-like shape. They are a delicacy in some cultures and are also ecologically important.
Cuttlefish:
Cuttlefish, related to squids and octopuses, have a unique, cuttlebone-shaped internal shell. They are highly intelligent and are popular in various cuisines.
Jellyfish:
Jellyfish are gelatinous, umbrella-shaped creatures found in oceans worldwide. While some species sting, others are harmless and an important part of marine ecosystems.
Corals:
Corals are marine invertebrates that form intricate, calcium carbonate structures, creating coral reefs. They provide habitat and shelter for a vast array of marine life.
Anemones:
Anemones are stinging polyps that resemble flowers, often found in marine environments. They are fascinating creatures and form important components of coral reefs.
Sea turtles:
Sea turtles are ancient reptiles adapted to life in the ocean. They are known for their distinctive shells and are critically important in maintaining the health of marine ecosystems.
Seabirds like gulls, pelicans, cormorants:
Seabirds, including gulls, pelicans, and cormorants, are well-adapted to life on the coast and at sea. They play a vital role in marine ecosystems, often diving for fish and contributing to nutrient cycling.
Phytoplankton (microscopic plants):
Phytoplankton are microscopic plants that form the foundation of marine food webs. They play a critical role in the carbon cycle and generate a significant portion of the world’s oxygen.
Zooplankton (microscopic animals):
Zooplankton are tiny, drifting animals in the ocean, including tiny crustaceans, larvae, and other small organisms. They are a crucial part of the marine food chain, serving as food for various marine creatures.
Benthic Organisms:
Benthic organisms refer to the organisms that live on or in the seafloor. They include a wide variety of invertebrates like crabs, worms, and shellfish, playing a vital role in recycling nutrients and maintaining seabed ecosystems.
Ecological Interactions and Relationships:
Within the continental shelf, intricate ecological interactions and relationships govern the balance of the ecosystem. Predatory-prey relationships, symbiotic interactions, and nutrient cycling are just a few examples of the complex dynamics that occur here. Predators regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining a healthy balance.
Symbiotic relationships, such as those between cleaner fish and host species, showcase the interdependence of marine life. Moreover, nutrient cycling, facilitated by decomposition and consumption, ensures the continuous flow of energy and nutrients throughout the ecosystem. Understanding these interactions is crucial for comprehending the resilience and sustainability of the continental shelf ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges:
Conservation of the continental shelf’s unique biodiversity is imperative to safeguard the health of our oceans and the planet. However, this habitat faces numerous challenges. Overfishing, habitat destruction from human activities like trawling, pollution, and climate change impacts such as ocean acidification and rising sea temperatures, are major threats.
Implementing effective conservation strategies involves establishing marine protected areas, sustainable fishing practices, reducing pollution, and addressing climate change. Collaboration among governments, scientific communities, and the public is essential to mitigate these challenges and ensure the sustainable management and conservation of the continental shelf and its precious marine life.

Final Words:
The continental shelf epitomizes the delicate balance of marine life, highlighting the intricate dance of nature beneath the waves. Its significance in preserving biodiversity, supporting livelihoods, and maintaining the ecological equilibrium cannot be overstated.
To secure a sustainable future, we must prioritize the protection and thoughtful management of this crucial marine habitat. Our actions today will determine the legacy we leave for generations to come. Let us rise to the challenge, unite in our efforts, and strive to conserve the continental shelf and its awe-inspiring array of marine life, for the prosperity of our planet and all its inhabitants.
Reference:
- https://sciencing.com/plant-animal-life-continental-shelf-6816368.html
- https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/ology-cards/180-continental-shelf
- https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/continental-shelf/

Zahra Makda
Growing up enjoying the beauty of my village, a good passion for nature developed in me from childhood. Following my passion for the natural world, I have chosen zoology for my graduation, during my undergraduate degree, I participated in many nature trails, bird watching, rescues, training for wildlife conservation, workshop, and seminars on biodiversity. I have a keen interest in invertebrate biology, herpetology, and ornithology. Primary interests include studies on taxonomy, ecology, habitat and behavior.









